Understanding The Fundamental Differences Between Teaching And Counseling
29th September 2023
Teaching and counseling are two distinct professions that play pivotal roles in shaping individuals' lives and fostering personal development. While both involve working with individuals to impart knowledge and facilitate growth, they differ significantly in their goals, methods, and approaches. If you are a teacher looking for career opportunities with counseling, you need to know the difference between the two. Read on to learn what teaching and counselling are as professions and the basic differences between them.
What Are Teaching and Counselling as Professions?
Teaching encompasses a fundamental part of a student's life, starting from childhood. Its primary purpose is to impart knowledge and understanding across a wide range of subjects and concepts, spanning from the elementary to advanced levels of education. A teacher plays a crucial role in helping students comprehend and learn these subjects while evaluating their performance.
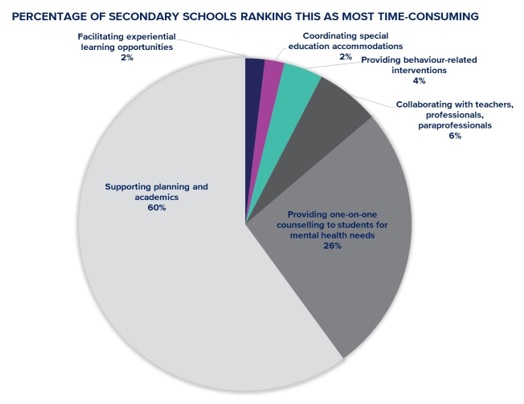
Source: peopleforeducation.ca
On the other hand, counseling, particularly guidance counseling, plays a distinct role in an individual's life. It focuses on helping individuals discover their interests, skills, and abilities, ultimately aiding them in making informed decisions about their future careers. In today's world, which offers a multitude of opportunities, the role of a career counselor holds significant importance in the lives of students as they navigate their academic and professional paths.
Major Differences between Teaching and Counselling
If you want to understand the professions better, here are some of the basic differences between the two:
1. Purpose and Goals
Teaching primarily focuses on the dissemination of knowledge and skills. The primary goal of teaching is to transfer information and cultivate understanding in a structured and systematic manner. Teachers aim to equip students with the necessary tools and competencies to succeed in academic or professional settings. The primary measure of success in teaching is typically the acquisition of knowledge and skills.
Counseling, on the other hand, is geared toward supporting individuals in addressing personal, emotional, or psychological challenges. The primary goal of counseling is to enhance the individual's emotional well-being, self-awareness, and personal development. Counselors work to facilitate introspection, coping mechanisms, and emotional growth. Success in counseling is often measured by improvements in mental and emotional health and overall life satisfaction.
2. Clientele Base
Teachers typically work with groups of students in educational institutions, ranging from preschools to universities. Their interactions are often structured around curricula and specific subjects or topics. The teacher-student relationship is more formal, and the focus is on academic content.
Counselors work with individuals or small groups of clients who seek assistance for personal, emotional, or psychological issues. Clients in counseling may range from children to adults, and the relationship is characterized by trust and confidentiality. The counselor-client relationship is typically less formal and more personal, with a focus on the client's well-being.
Hey, do you follow us on Social Media? We regularly share upgraded educational content, tips, feedback and more. Check us out by clicking the profiles here - Facebook / Twitter / LinkedIn / Pinterest / Instagram / YouTube
3. Methods and Approaches
Teaching involves a structured approach to instruction, where teachers follow predefined curricula and lesson plans. The emphasis is on presenting information, explaining concepts, and assessing student understanding through tests and assignments. Teachers often use lectures, presentations, and classroom activities to achieve their educational goals.
Counseling employs a more dynamic and client-centered approach. Counselors use active listening, empathy, and open-ended questions to help clients explore their feelings, thoughts, and behaviors. Therapeutic techniques such as cognitive-behavioral therapy, psychoanalysis, or art therapy may be employed based on the client's needs. The focus is on self-discovery and personal growth.
4. Relationship Dynamics
The teacher-student relationship is characterized by authority and expertise. Teachers hold the role of knowledge providers and authority figures in the classroom. While they aim to create a positive and supportive learning environment, the dynamic is inherently hierarchical.
The counselor-client relationship is built on trust, empathy, and collaboration. Counselors do not impose solutions but rather guide clients in exploring their issues and finding their answers. The counselor's role is that of a facilitator and a partner in the client's journey towards self-improvement.
5. Outcome and Evaluation
The success of teaching is often measured through assessments, tests, and evaluations that determine the level of understanding and mastery of the subject matter. Grades and academic achievements are common indicators of success in teaching.
Counseling success is evaluated based on improvements in the client's mental and emotional well-being, coping skills, and the resolution of personal issues. Success is often subjective and personalized, as it depends on the client's individual goals and progress.
Be Wise and Know What It Takes
Teaching and counseling are distinct professions with different purposes, client dynamics, methods, and evaluation criteria. Teaching revolves around the dissemination of knowledge and academic skill development, while counseling focuses on personal growth, emotional well-being, and addressing psychological challenges. Understanding these fundamental differences and pursuing a Certificate in Counselling Course for Teachers is essential for those aspiring for educational counselling careers and contributing to the holistic development of individuals and communities.
Written By : Sanjana