School Absenteeism And School Refusal Behaviour In Students: A Matter Of Concern
11th August 2023
School absenteeism and school refusal behavior among youngsters have garnered significant attention due to their potential negative impact on educational attainment, psychological well-being, and overall development. Read on to gain a comprehensive overview of the concepts, causes, consequences, and interventions related to school absenteeism and school refusal behavior. Additionally, learn some measures that can be taken to prevent and eradicate this issue bit by bit.
What Do You Understand By School Absenteeism And Refusal?
School absenteeism refers to a student's intentional and unauthorized absence from school. It can be categorized as truancy, where students skip classes without parental knowledge, and chronic absenteeism, characterized by prolonged and frequent absences. It is often a serious physical and mental health concern for children and adolescents alike. Research has suggested that absenteeism usually is the key factor for perilous sexual behavior, suicide attempt, teenage pregnancy, violence, and substance abuse. Being absent from school can also result in several psychiatric problems.
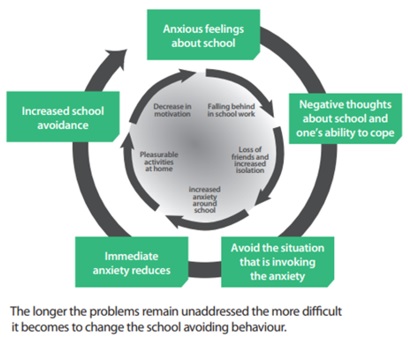
Source: portobellohighschool.org.uk
School refusal behavior, on the other hand, goes beyond mere absenteeism, encompassing emotional distress and avoidance of school due to anxiety, fear, or other psychological factors. High levels of reluctance and distress to go to school are known as school refusal. Young people often appear unhappy the morning they are supposed to go to school. This is different from truancy as family and friends do know that a child is not attending school despite their best efforts.
Causes and Factors Of Absenteeism And Refusal Behaviour
Numerous factors contribute to school absenteeism and refusal behavior. Some of the most common ones include:
- Academic challenges, such as learning disabilities or low achievement, can lead to avoidance as students feel overwhelmed by their inability to meet academic expectations.
- Social factors like bullying, peer conflicts, or a lack of social support can contribute to negative school experiences, prompting avoidance.
- Psychological issues like anxiety disorders, depression, and separation anxiety can manifest as refusal behavior.
Further research is needed to delve into the underlying causes and mechanisms driving school refusal behavior. Longitudinal studies can provide insights into the persistence and long-term consequences of these behaviors. Additionally, interventions should be continually refined based on emerging evidence and evolving educational landscapes.
What Consequences Can This Have On Students?
The consequences of these behaviors are far-reaching. Academic repercussions include falling behind in coursework, reduced educational attainment, and limited future opportunities. Psychologically, youth may experience increased anxiety, depression, and feelings of isolation. Long-term effects can include decreased job prospects and a higher risk of engaging in delinquent or risky behaviors.
Hey, do you follow us on Social Media? We regularly share upgraded educational content, tips, feedback and more. Check us out by clicking the profiles here - Facebook / Twitter / LinkedIn / Pinterest / Instagram / YouTube
How Can You Address School Absenteeism And Refusal Behaviour?
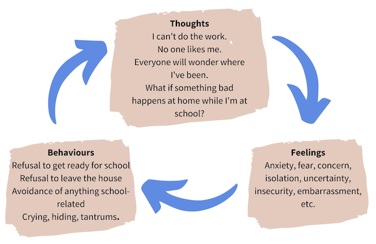
Source: blog.studybugs.com
Addressing school absenteeism and refusal behavior requires a multi-faceted approach involving schools, families, and mental health professionals. Early identification and intervention are crucial. Here are some things family and society can do to tackle this grave issue:
- Educational Institutions
Schools can implement strategies like positive school climate promotion, offering engaging curricula, and providing counseling services. Collaboration between teachers, parents, and counselors can help identify triggers and develop targeted interventions. Cognitive-behavioral therapy and exposure therapy are effective psychological interventions for managing anxiety-related refusal behavior.
- Family Dynamics
Family plays a vital role in shaping a child's attitude toward school. Overprotective parenting or enabling avoidance behaviors inadvertently reinforces refusal behavior. Conversely, family involvement in treatment can facilitate progress. Addressing familial issues, fostering open communication, and promoting a supportive environment are essential components of successful intervention.
- Technology and Virtual Learning
The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the role of technology in education. While virtual learning can mitigate some challenges related to school refusal behavior, it may exacerbate feelings of isolation and detachment. Schools and families need to strike a balance between utilizing technology for education and ensuring students maintain social connections and a sense of belonging.
- Cultural and Socioeconomic Understanding
Cultural and socioeconomic factors influence school attendance. Cultural attitudes towards education, as well as economic circumstances, can impact a family's prioritization of schooling. Understanding these influences is crucial for tailoring interventions that consider the unique context of each student.
- Safe And Inclusive Environment
Preventing school absenteeism and refusal behavior necessitates a proactive approach. Schools can implement attendance tracking systems, establish early warning systems for potential issues, and offer training for teachers to recognize signs of distress. Creating a safe and inclusive environment where students feel valued and supported can deter avoidance behaviors.
Prevent This Issue For Better Future
School absenteeism and school refusal behavior have wide-ranging implications for youth development. A holistic approach that involves schools, families, and mental health professionals is necessary to address this behavior effectively. Moreover, taking care of someone who is experiencing school absenteeism and school refusal behavior might be daunting and exhausting. Thus it is essential to pursue a Post Graduate Diploma in Counselling for Teachers or parents to be able to learn to take care of yourselves and model good-self care for their children. By understanding the complexities and contributing factors, educators and caregivers can work collaboratively to ensure that all youngsters have the opportunity to thrive academically and emotionally.
Written By : Sanjana